Computer parts | components of computer
Introduction:- Computer parts are the personal components that use for make a computer. Each computer part has specific role in the overall work of the computer. here some of the important computer parts and their work functions.
Central Processing Unit (CPU): CPU is know Always known as the brain of the computer. It work most of the calculations and instructions that allow the computer to run programs and perform tasks. CPU has an an arithmetic logic unit (ALU) that carries out calculations, and a control unit which coordinates the activities of the computer other parts.
CPU work on wide range of tasks, like executing software instructions, handling data processing, managing input and output operations, and coordinating the activities of other hardware parts. It explain and comply instructions stored in the computer's memory, performing arithmetic, logical, and control operations. let's explore some key aspects of a central processing unit.
- Control Unit (CU): This is responsible for fetching program instructions from the computer memory, decoding them, and managing the execution of these instructions. It coordinates the activities of different CPU parts to ensure all that order are executed in the correct instruct
- Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU): It work mathematical calculations and logical operations. ALU can do add, subtract, multiply, divide, compare numbers, perform logical operations, and more. It carries out these operations based on the instructions provided by the control unit.
- Registers: Registers are small and high speed memory locations within the CPU which store data and instructions that the CPU needs to access fast. They hold operands (data on which calculations are performed), instructions, and intermediate results while processing. Registers allow for quick access to data compared to accessing memory.
- Cache: Cache is a small and fast memory unit located to the CPU. It store together accessed data and instructions, reducing the time required to fetch them from the computer main memory. Caches increase the CPU overall performance by minimizing memory access delays.
- Clock Speed: The clock speed refer to the frequency at which the CPU operates and executes instructions. It is measured in cycles per second, typically in Ghz. a higher clock speed generally means the CPU can perform more instructions in a given time, resulting in quick processing.
- Cores: Modern and faster CPU always have multiple core, which are individual processing units within a single physical chip. every core can independently execute directions allowing for parallel processing and improved performance in tasks that can be divided into multiple threads.
Different processing unit are designed with varying architecture, technology and features. faster CPU manufacturers include Intel and AMD, who produce CPU for different computing devices, running from personal computer and laptop to server and mobile devices.
In Brief summary, the CPU is a crucial component of a computer system that performs the greater part of processing tasks. It execute instruction, performs calculation, manage data, and coordinate the activities of other hardware parts to provide the necessary computing power for running software application.
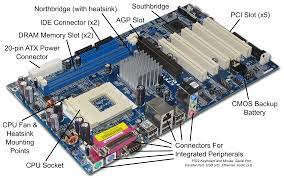
Motherboard: The computer motherboard, also known as the main board or system board. it's a central printed circuit board (PCB) that connect and hold together important parts of a computer. It work as a communication hub and allowing different hardware components to interact and work together flawlessly. The motherboard provides electrical and logical connection for different devices, like the CPU, memory, storage, ram, and other peripherals. here are some key aspects of a computer motherboard.
- Form Factor: The form factor represent to the physical size, shape, and layout of the motherboard. Common form factors add ATX, Micro ATX and Mini ITX. The form factor decides the compatibility and size of the motherboard, it affect the cabinet and other components that can be installed.
- CPU Socket: The motherboard features a CPU socket or slot where the processor (CPU) is installed. The CPU socket type should match the specific CPU model and socket or slot compatibility to ensure proper functioning. Different CPU manufacturers may have their own socket or slot design, like as Intel LGA (Land Grid Array) or AMD PGA (Pin Grid Array).
- Memory Slots: The motherboard has slots for installing system memory modules, like as DIMM (Dual In-Line Memory Modules). All memory slot are made for support specific types of memory such as DDR4 or DDR5. The number of memory slots and the maximum memory capacity supported by the motherboard may vary.
- Expansion Slots: Expansion slot allow for the installation of additional expansion cards, like as graphics cards, sound cards network card, and storage controller. the most regular expansion slot is the PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect ) slot which are available in different size like as x1, x4, x8, x16, x32 depending on the data transfer capacity need of the installed card.
- Storage Interfaces: Motherboard provide connector and interface for connecting storage parts like as hard disk drives (HDDs) and solid-state drives (SSDs). Common storage interfaces include SATA (Serial ATA). The number of available connectors may vary depending on the motherboard model.
- I/O Port: motherboard has various I/O (Input/Output) port for connect external components such as USB port, audio jack, Ethernet port, Display Port for video output, types of I/O port can be change depending on the motherboard models and brand such a intel, Asus, Gigabytes and MSI
- Chipset: Motherboard has a chipset which comprises of integrated circuits that operate the communication between the CPU, memory, expansion cards, and other parts. The chipset decides the advantages and capabilities of the motherboard, such as the number of supported USB ports, PCI lanes, and overall computer speed.
- Power Connectors: Motherboard has power connector for receive power from the SMPS (Switched Mode Power Supply) and split that to various parts on the motherboard. primary power connector has a 24 pin ATX connector and there may be extra power connector for processor power (4 pin or 8 pin) and display card (6 pin or 8 pin).
Motherboard acts as the foundation of a computer system, providing the necessary connections and infrastructure for all the essential parts to function together. When select a motherboard that is crucial to consider factor such as compatibility with the processor and RAM, expansion options, and connectivity features to ensure best performance and flexibility for your computing needs.
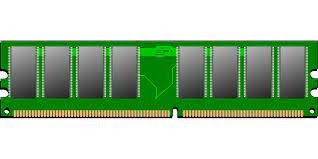
Random Access Memory (RAM): RAM is a type of computer memory that provide capacity for data that is effectively being used by the computer processor. It is a unpredictable memory, meaning its content are lost when the computer is powered off or restarted. here are some key aspects of computer RAM.
- Function: RAM serve as a temporary workspace for data and instructions that the CPU needs to access quickly. When a program is running its data and instruction are loaded into RAM from the computer storage devices (like the hard drive or SSD) to enable faster access and processing by the CPU.
- Access Speed: RAM is much faster than storage devices like hard drives or SSDs. It offers quick access to data, allowing the CPU to read and write information rapidly. the speed of RAM is read in MHz or GHz, pointing the number of cycles per second at which the RAM can operate.
- Capacity: RAM efficiency refer to the amount of data that can be stored in RAM. that is regularly read in gigabytes (GB) or terabytes (TB). The more RAM a computer has the more data it can store for quick access or process, it can improve overall computer performance.
- Types of RAM: There are different type of RAM such a DDR4 (Double Data Rate 4), DDR3, and older generations like DDR2 and DDR. Each generation offer improved speed and performance compared to its ancestor. The specific type of RAM supported by a computer depends on the motherboard and CPU compatibility.
- RAM Modules: RAM is installed in the computer using memory modules. The most common module form factor is the DIMM (Dual In-Line Memory Module). These modules are inserted into slots on the motherboard. The number of RAM slot on a motherboard decide the maximum amount of RAM that can be installed.
- Memory Channels: Some motherboard support multiple RAM channel such as dual-channel or quad-channel memory configurations. These configurations allow to increased memory bandwidth and improved performance by accessing multiple memory modules simultaneously.
- Virtual Memory: In addition to physical memory computer also use virtual memory, that is a part of the computer storage (like the hard drive) used as an extension of memory. When physical memory become full, the computer swaps data between RAM and the hard drive, which can slow down performance.
It is significant to note that the amount of RAM demand for optimal performance depends on the specific needs and usage patterns of the computer. For general work such as web browsing, word processing, and multimedia playback, 8GB to 16GB of memory is enough. However, memory-intensive task like video editing, gaming, or running virtual machine may benefit from 16GB or more.
Overall, RAM plays a critical role in computer performance by providing fast and temporary storage for actively used data and instructions. that allow the CPU to quickly access information resulting in smoother multitasking, faster program execution, and an overall more responsive computing experience.
Hard Disk Drive (HDD) or Solid State Drive (SSD): computer hard disk also known as a HDD (hard disk drive) and is a non-uncertain storage device use for store and retrieve digital data. It is one of the primary storage select in modern computer and is capable of keeping a big amount of data even when the computer is turned off. here are some key aspects of a computer hard disk
- Storage Capacity: PC Hard disks are available in different storage capacity running from a few hundred gigabytes (GB) to multiple terabytes (TB) or even petabytes (PB). The capacity determines how much data the hard disk can store. As technology advances the storage capacity of hard disks continues to increase.
- Physical Structure: A hard disk is made up of one or more spinning magnetic disks called platters. These platters are coated with a magnetic material that allows data to be written and read using read/write heads. The platters are vertical on a spindle and rotate at high speeds, basically between 5,400 to 15,000 revolutions per minute (RPM).
- Read/Write Heads: The read/write heads are tiny electromechanical devices that float just above or below the surface of the spinning platters. They are responsible for reading data from and writing data to the platters. The heads move rapidly across the platter's surface, accessing the desired data.
- Data Access and Transfer Speed: The speed at which information can be gotten and moved from a hard disk is evaluated in terms of the rotational speed of the platter and the data transfer ratings. Higher RPM and data transfer rates result in faster data access and faster file transfer speeds.
- Interfaces: Hard disks are fitted to the PC motherboard by many interfaces such as Serial ATA (SATA) or the older Parallel ATA (PATA) interface. These interfaces decide the speed and compatibility of the hard disk with the computer. Newer interfaces such as SATA III (SATA 6Gbps), provide faster data transfer speed compared to older versions.
- Form Factors: Hard disks accessible in various actual sizes or structure factors, like 3.5-inch and 2.5-inch. The form factor determines the physical dimensions of the hard disk and is important for compatibility with the computer's chassis or storage bays.
- Fragmentation and File System: Over time, data on a hard disk can become fragmented, meaning parts of files are scattered across different areas of the disk. File systems, such as NTFS or HFS+ deal the organization and retrieval of files on the hard disk, including taking care of discontinuity.
- Solid-State Drives (SSDs): While hard disks are the Conventional storage solution, solid-state drives (SSDs) have become increasingly popular. SSDs use flash memory technology instead of spinning platters, offering faster data access, higher speeds, and better shock resistance. SSDs are more expensive per unit of storage compared to hard disks but are commonly used as boot drives or for storing frequently accessed data.
It is worth noting that hard disks have moving parts which make them powerless to mechanical disappointment. Regular backups and proper handling are important to protect data stored on hard disks.
In summary, a computer hard disk is a storage device that uses spinning platters and read/write heads to store and retrieve data. it provide big storage capacities and is widely use for storing OS, software, files & folder, and other data in desktop computer, laptop, server, and other devices.
Graphics Processing Unit (GPU): A GPU is a specific electronic circuit that speeds up the creation and rendering of images, videos, and animations. While CPUs (Central Processing Units) are designed for general-purpose computing, GPUs are specifically optimized for parallel processing tasks related to graphics rendering and computation.
Originally, GPUs were basically used in computer graphics, powering video games, 3D modeling, and other visually escalated applications. However their high computational power and ability to manage multiple tasks all the while have led to their adoption in various other fields such as scientific research, artificial intelligence, machine learning, and cryptocurrency mining.
The major difference between a CPU and a GPU lies in their architecture and design theory. CPUs typically have a few powerful cores optimized for sequential processing tasks, while GPUs consist of numerous smaller cores (sometimes in the hundreds or thousands) optimized for parallel processing. This equal architecture enables GPUs to perform operations on multiple data elements all the while, making them extremely efficient for tasks that can be broken down into smaller, independent operations. GPUs are particularly beneficial for computationally intensive applications, such as.
- Graphics Rendering: GPUs excel at rendering complex 3D scenes, applying textures, lighting, and other visual effects in real-time. They can handle massive amounts of geometric and pixel calculations required for high-quality graphics.
- Machine Learning: Deep learning algorithms often involve performing calculations on large matrices and neural networks. GPUs can dramatically speed up these computations by parallelizing matrix operations, resulting in faster training and inference times.
- Scientific Simulations: Hard scientific simulations, such as weather modeling, fluid dynamics, and molecular dynamics, require significant computational power. GPUs enable researchers to simulate and analyze these complex systems more efficiently.
- Cryptocurrency Mining: Some cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, rely on complex mathematical calculations to validate transactions and secure the network. GPU has been widely embraced for mining cryptocurrencies because of their high computational power.
To utilize the computational power of a GPU, software applications need to be specifically programmed to leverage parallel processing capabilities. famous programming framework such as CUDA (Compute Unified Device Architecture) by NVIDIA and OpenCL (Open Computing Language) give API that permit developer to write code that can make good on GPU.
In recent years, GPU have become more adaptable and powerful, with progressions in technology permitting for increased memory capacity, higher clock speeds and improved energy efficiency. As a result GPU continue to play a big role in speeding up various computationally demanding tasks across different industries.
Switched Mode Power Supply (SMPS): SMPS stand for Switched-Mode Power Supply. It's a kind of power supply unit use in PC and electronic device to convert and regulate electrical power from the primary power source (such as an electrical outlet) into the required voltage and current levels for the parts inside the computer.
The main work of an SMPS is for efficiently change high-voltage alternating current (AC) power into low-voltage direct current (DC) power. This changes is necessary therefore most PC parts such as the Processor, motherboard, hard disk, and graphic card, operate on low-voltage DC power. here is a breakdown of the key components and working principles of an SMPS.
- Rectification: The first step in the SMPS is rectification, where the AC power from the main source is converted into pulsating DC power. This is achieved using a rectifier, typically a bridge rectifier, which converts the AC input into a varying DC voltage.
Filtering: After rectification, the pulsating DC voltage undergoes filtering to smoothen out the variations and create a more stable DC voltage. Capacitors are used for this purpose, which store charge during high voltage period and release it during low voltage periods, resulting in a more continuous and stable output voltage8
Switching: The core principle of an SMPS involves switching. The isolated DC voltage is taken care into a high-frequency oscillator, often a transistor or a MOSFET (Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor). The oscillator quickly switches the DC voltage on and off at a high recurrence (typically tens or hundreds of kilohertz).
- Transformation: The switched voltage is then fed into a transformer, which convert the high-frequency DC voltage into a lower voltage level suitable for the computer components. The transformer consists of primary and secondary windings, and the ratio between the windings determines the output voltage.
- Rectification and Filtering (again): The transformed voltage is rectified and filtered once again to produce a smoother and regulated DC output voltage. This ensures that the voltage remains stable even with varying input voltage or load conditions.
- Voltage Regulation: SMPS units include a voltage regulation circuit that monitors the output voltage and adjusts it as necessary to maintain a stable and accurate voltage level. This regulation is crucial to protect the computer components from voltage fluctuations and ensure their proper operation.
The benefits of SMPS over traditional linear power supplies incorporate higher efficiency, smaller size, lighter weight, and the ability to handle a wide range of input voltages. The switching nature of SMPS allows for greater efficiency as the transistors operate in an on/off fashion, minimizing power loss. Additionally, the compact size of SMPS units makes them well-suited for space-constrained devices like computers.
Anyway, SMPS units also generate some amount of electrical noise due to their switching operation, which needs to be mitigated through proper shielding and filtering. Overall, SMPS units are widely used in computers and electronic devices due to their efficiency, reliability, and ability to provide stable power to the components.
Keyboard: computer keyboard is an input device that allow user to input alphanumeric character, symbols, and commands into a computer. that is one of the main ways users interact with their computer and permitting them to type, navigate, and execute various instruction. here are the key component and features of a computer keyboard.
- Key Layout: Computer keyboards typically follow the QWERTY layout, named after the first six letters on the top row. The format also includes numeric keys, function keys (F1-F12), modifier keys (Shift, Ctrl, Alt), and special keys for functions like Enter, Back space, and Space bar.
- Key Switches: The keys on a keyboard are mounted on individual switches beneath them. There are different types of key switches, each offering a different typing experience. The most common types are membrane switches, scissor switches, and mechanical switches. Mechanical switches are favored by enthusiasts for their tactile feedback and durability.
- Function Keys: The function keys (F1-F12) provide shortcut to many system functions and commands. They are often used in conjunction with modifier keys (Ctrl, Alt) to trigger specific actions like saving, printing, opening applications, adjusting volume, and more.
- Numeric Keypad: Many keyboards have a separate numeric keypad on the right side, permitting user to input numbers quickly. it is especially useful for tasks that involve a lot of numerical data entry, like spreadsheet and accounting software.
- Special Keys: Keyboards often include special keys dedicated to specific functions. These can include multimedia keys for controlling media playback, navigation keys for moving the cursor, Windows key for accessing the Start menu (on Windows systems), and additional programmable keys for custom shortcuts.
- Connectivity: Keyboard can be connected to a PC using different interfaces, such as USB (Universal Serial Bus), PS/2 (older interface), or wireless connections like Bluetooth. USB has become the most common connection method due to its ingenuity and broad similarity.
- Keyboard Layouts: While the QWERTY layout is the most widely use different countries and languages may have their own keyboard layout to accommodate specific character and symbols. Examples include AZERTY (used in France and Belgium) and QWERTZ (used in Germany and some other European countries).
- Ergonomics: Some keyboards are designed with ergonomic considerations to promote comfortable typing and reduce strain on the hands and wrists. These keyboards may have a split design, curved layout, or built-in wrist rests to provide better support and prevent repetitive strain injuries.
Modern keyboard often add additional features such as backlighting for typing in low-light environment, programmable large scale keys for creating custom shortcuts, and multimedia controls for easy access to media playback.
Generally, the computer keyboard is an fundamental input device that enables user to interact with their PC productively and successfully by inputting text, executing command, and exploring through various applications and interfaces.
Mouse: Mouse: PC mouse is an input device that permit user to manipulate the movement of a cursor on a computer screen or different graphical consumer interface (GUI). It is normally held in the hand and moved across a flat surface to control the cursor's position and perform various actions. here are the key components and features of a computer mouse.
- Cursor Control: The main work of a mouse is to control the movement of the cursor at the screen. while the mouse is moved, sensor within the device locate the movement and translate it into corresponding cursor motion. The cursor can be moved on a level plane (x-axis) and vertically (y-axis) based at the mouse's bodily movement.
- Buttons: standard mouse has at least two buttons left-click and right-click. The left-click button is used for selecting objects, clicking on links, and executing primary actions. The right-click button typically opens contextual menus with additional options. Some mice may have additional buttons on the sides, which can be customized for specific functions or shortcuts.
- Scroll Wheel: The scroll wheel is a wheel located between the left and right button. that permit user to scroll up and down on documents, web pages, and other content without the need for manual dragging. In some mice, the scroll wheel can also be shifted left or right for even scrolling.
- Connectivity: Mice can be connected to a computer using different interfaces. The most common connection types are wired USB (Universal Serial Bus) and wireless (usually using Bluetooth or RF technology). Wired mice are directly connected to the computer via a cable, while wireless mice communicate with a receiver plugged into the computer or directly with built-in wireless capabilities.
- Optical or Laser Sensors: The movement of the mouse is tracked through optical or laser sensors located on the underside of the tool. Optical sensors use an LED light and a camera to capture images of the surface, while laser sensors use laser light for more precise tracking. These sensors detect the surface texture and movement, converting it into cursor movement on the screen.
- DPI (Dots Per Inch) Sensitivity: Mouse sensitivity is often measured in DPI, representing the number of pixels the cursor moves on the screen for each inch the mouse physically moves. Higher DPI settings result in faster cursor movement, while lower settings provide more precise control. Many mice allow users to adjust the DPI sensitivity to suit their preferences.
- Gaming Mice: Gaming mice are specialized mice designed for gaming enthusiasts. They often have additional programmable buttons, adjustable weights for customization, and higher DPI settings for faster and more accurate cursor movement. Gaming mice may also feature customizable RGB lighting for aesthetics.
- Ergonomics: Ergonomic mice are designed to provide more comfort and reduce the risk of repetitive strain injuries. They often feature a contoured shape that fits the natural hand position, additional support for the wrist or thumb, and materials that reduce grip fatigue.
The computer mouse revolutionized the way users have interaction with graphical user interfaces, making it less complicated and extra intuitive to navigate and have interaction with virtual content. Its versatility and ease of use have made it a essential input tool in almost all modern computers.












Comments
Post a Comment
Please do not enter any spam link in comment box